
Introduction
Overview of the Pyramids of Giza
The Pyramids of Giza, standing majestically on the Giza Plateau near Cairo, are timeless symbols of ancient Egyptian civilization. Built over 4,500 years ago, they continue to be a source of fascination due to their remarkable architecture and alignment with celestial bodies. Notably, the Great Pyramid of Khufu showcases not only engineering prowess but also represents the grandeur of a civilization deeply invested in the afterlife.
Significance of Ancient Burial Practices
Ancient Egyptian burial practices were intricately connected to their beliefs about death and the afterlife, making them significant on multiple levels. Here are some key points:
- Spiritual Beliefs: The preservation of the body through mummification reflected the belief in an eternal life beyond death.
- Cultural Identity: These practices established a strong sense of identity and continuity for the community.
- Artistic Expression: Elaborate tombs and artifacts illustrate the ancients’ artistry and dedication to their gods and deceased rulers.
Personal experiences exploring these ancient sites often evoke a strong sense of connection to the past, as visitors reflect on the complexities of life and death that these remarkable structures represent.
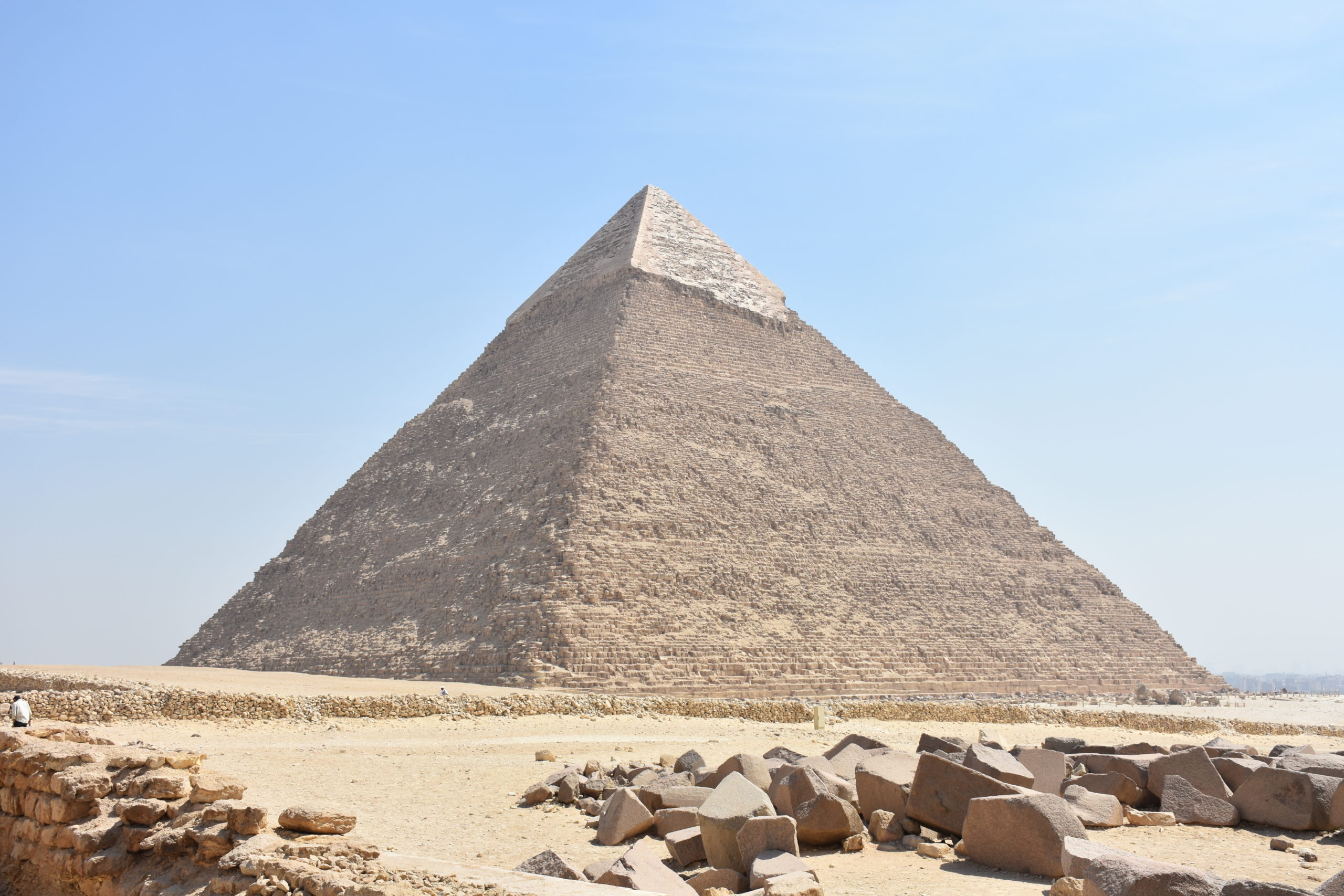

History of the Pyramids
Construction Timeline
The construction of the Pyramids of Giza unfolded over several decades, primarily during the Fourth Dynasty of the Old Kingdom (circa 2580-2560 BCE). Key milestones include:
- Khufu’s Great Pyramid: Constructed first, it took approximately 20 years.
- Khafre’s Pyramid: Built next, utilizing nearby limestone for a smooth finish.
- Menkaure’s Pyramid: The smallest pyramid, completed later with unique granite.
Each pyramid showcases the technological advancements of its time.
Purpose of the Pyramids
The purpose of these grand structures went beyond mere burial places. They served multifaceted roles:
- Tombs of Pharaohs: Central to each pyramid’s design was the exaltation of deceased rulers, ensuring their safe passage to the afterlife.
- Religious Symbols: They represented stairways to the heavens, aligning with the belief in divine ascension.
- Societal Unity: These monumental projects galvanized resources, labor, and community spirit, reflecting the strength of ancient Egyptian society.
Reflecting on these elements sparks curiosity about how ancient civilizations united their resources and beliefs to leave lasting legacies. The pyramids tell stories of ambition, faith, and devotion that still resonate today.
Burial Practices in Ancient Egypt
Mummification Process
Delving deeper into ancient burial practices, the mummification process was a meticulous art, designed to preserve the body for eternity. Here’s a glimpse into the steps involved:
- Removal of Internal Organs: Organs were carefully extracted and stored in canopic jars.
- Drying the Body: The body was covered in natron, a natural salt, to dehydrate it.
- Wrapping: Finally, the body was wrapped in linen, often with amulets placed within the layers for protection.
Experiencing this at the Egyptian Museum provides a profound appreciation for their dedication to preserving life after death.
Beliefs about the Afterlife
The ancient Egyptians believed the afterlife was a continuation of earthly life, filled with challenges and rewards. Some core beliefs included:
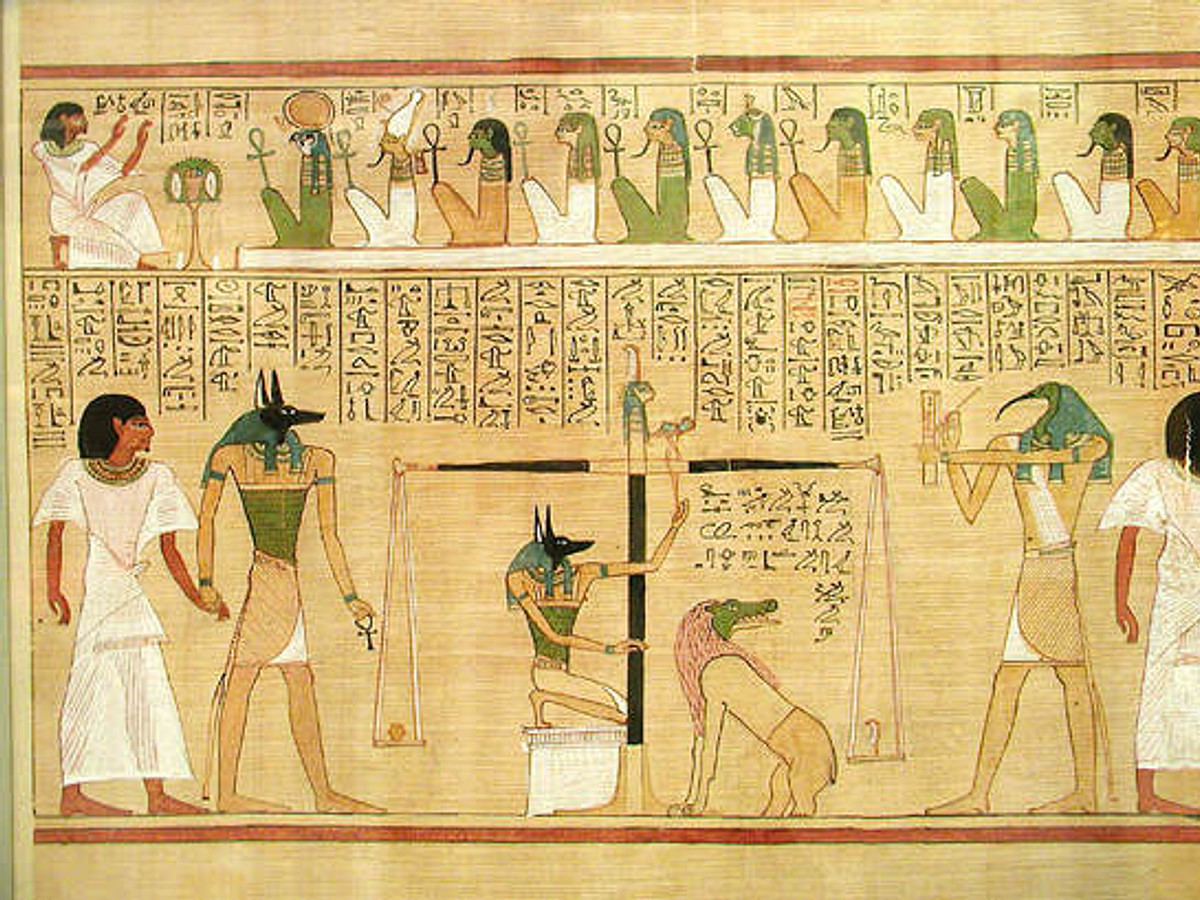
- Judgment Day: The deceased would face Osiris in a judgment ceremony, weighing their heart against the feather of Ma’at (truth).
- Eternal Paradise: Success in judgment meant entering the Field of Reeds, a heavenly utopia.
These beliefs highlight a rich spiritual culture, where immortality was tied to moral integrity and cosmic balance. Reflecting on these faiths allows us to appreciate the profound depth of human curiosity regarding life beyond death.

Architectural Features of the Pyramids
Structure and Design
Transitioning from the beliefs surrounding the afterlife, the architectural features of the Pyramids of Giza illustrate the Egyptians’ profound understanding of engineering and design. The construction features include:
- Precision Alignment: The pyramids are aligned with remarkable accuracy to the cardinal points.
- Carved Limestone: The outer casing of fine white limestone gave the pyramids a brilliant appearance in sunlight.
- Gradual Step Design: Early pyramid designs used a stepped structure, which eventually evolved into the smooth-sided pyramids we recognize today.
Witnessing the pyramids firsthand reveals just how ambitious these ancient builders were.
Interior Layout
Inside, the pyramids hold their own mysteries and intricacies. Typically, the interior layouts included:
- Burial Chambers: Centrally located and only accessible by narrow passages.
- Grand Galleries: Large ascents that guided tomb robbers away from the burial chamber.
- Relieving Chambers: Ingeniously designed to distribute weight and prevent collapse.
Exploring these interiors brings to life the ingenuity and artistry of a civilization that valued the afterlife, making each visit a journey through history and human creativity.

Tomb Contents and Artifacts
Burial Chambers
Continuing from the intricate layouts of the pyramids, the burial chambers housed the remains of pharaohs and were designed with meticulous care. These chambers often included:
- Granite Sarcophagi: Heavy stone coffins that held the mummified body, symbolizing the pharaoh’s strength.
- Wall Decorations: Intricate carvings and paintings depicting scenes from the afterlife, meant to aid the deceased on their journey.
Walking through these chambers evokes a sense of reverence, as one contemplates the grandeur of royal burials.
Treasures Found in the Pyramids
Notably, the contents of the tombs included a trove of artifacts intended for the afterlife, such as:
- Golden Jewelry: Items of immense value, showcasing the craftsmanship of ancient artisans.
- Everyday Objects: Pottery, tools, and furniture designed to ensure comfort in the afterlife.
- Funerary Offerings: Food and goods believed to sustain the pharaoh in their next life.
Uncovering these treasures not only enriches our understanding of ancient Egyptian culture but also elevates the mysteries of how life and death were interconnected in their society. Each artifact tells a story, inviting us to ponder the legacy of those who once adorned these majestic tombs.

Modern Discoveries and Excavations
Recent Studies and Findings
Transitioning from the treasures unearthed within the pyramids, modern discoveries continue to reveal astonishing insights. Recent studies include:
- Ground-Penetrating Radar Scans: These have uncovered hidden chambers within the Great Pyramid, prompting intrigue about undiscovered artifacts.
- DNA Analysis: Researchers are examining mummies to trace lineage and health, offering glimpses into the lives of ancient Egyptians.
Visiting excavation sites often brings a palpable sense of excitement as the past intertwines with the present.
Impact on Archaeology and History
These ongoing discoveries significantly impact archaeology and historical understanding. They:
- Refine Historical Timelines: New findings challenge existing narratives and timelines of Egypt’s dynasties.
- Enhance Preservation Techniques: Techniques developed from these studies help protect artifacts and sites for future generations.
- Inspire Global Interest: The fascination generated revitalizes interest in ancient civilizations, encouraging educational pursuits.
Through these modern explorations, we deepen our appreciation for the ancient world and its continuous influence on contemporary society. Each excavation reflects our enduring quest to understand our shared human history, bridging the gap between ancient wisdom and modern knowledge.

Legacy of the Pyramids
Cultural Influence
Building upon the ongoing discoveries, the legacy of the Pyramids of Giza extends far beyond their physical presence. They have left a profound cultural influence, seen in:
- Art and Literature: Many contemporary artists and writers draw inspiration from the themes of immortality and grandeur present in the pyramids.
- Architecture: Modern designs often pay homage to these ancient structures, reflecting their enduring impact on architectural trends.
Experiencing this cultural resonance, one can appreciate how these monuments have captured human imagination across generations.
Tourist Attractions
Moreover, the pyramids serve as iconic tourist attractions, drawing millions annually. Key aspects include:
- Guided Tours: Visitors gain insights from knowledgeable guides, enhancing their understanding of Egypt’s rich history.
- Cultural Events: Festivals and reenactments often celebrate the pyramids, bringing the past to life for modern audiences.
- Photographic Opportunities: The stunning landscape provides a perfect backdrop for unforgettable memories.
Each visit offers a chance to connect with ancient history, creating a sense of wonder and reverence for the enduring legacy of the Pyramids of Giza. This combination of culture and tourism fosters a vibrant dialogue between past and present, emphasizing the importance of these magnificent monuments in today’s world.

Conclusion
Recap of Ancient Burial Practices
Reflecting on the journey through ancient burial practices, it’s clear that mummification, elaborate tombs, and rich artifacts were integral to the Egyptians’ beliefs in the afterlife. These customs not only highlighted their spiritual convictions but also demonstrated their advanced understanding of preservation and reverence for the dead. Each burial practice reveals a society deeply invested in immortality and legacy.
Significance of the Pyramids of Giza
The Pyramids of Giza stand as a testament to the ingenuity and ambition of ancient Egyptian civilization. Their significance lies in:
- Architectural Marvels: Awe-inspiring structures that continue to defy modern engineering assumptions.
- Cultural Heritage: Rich symbols of ancient beliefs, art, and social structure.
- Global Influence: Their lasting impact inspires countless individuals and cultures around the world.
As these magnificent edifices continue to capture imaginations, they remind us of the profound connections between past and present, inviting us to explore the mysteries of human existence and our enduring quest for meaning. Each visit to these ancient wonders serves as a powerful reminder of our shared heritage, encouraging a sense of respect and wonder for what has come before.













